Pressure Die casting is a metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high or low or vacuum pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the process. Most die castings are made from ferrous & non-ferrous metals, specifically steel, zinc, copper, aluminium, magnesium, lead, pewter, and tin-based alloys. Depending on the type of metal being cast, a hot- or cold-chamber machine is used.
The casting equipment and the metal dies represent large capital costs and this tends to limit the process to high-volume production. Manufacture of parts using die casting is relatively simple, involving only four main steps, which keeps the incremental cost per item low. It is especially suited for a large quantity of small- to medium-sized castings, which is why die casting produces more castings than any other casting process. Die castings are characterized by a very good surface finish (by casting standards) and dimensional consistency.
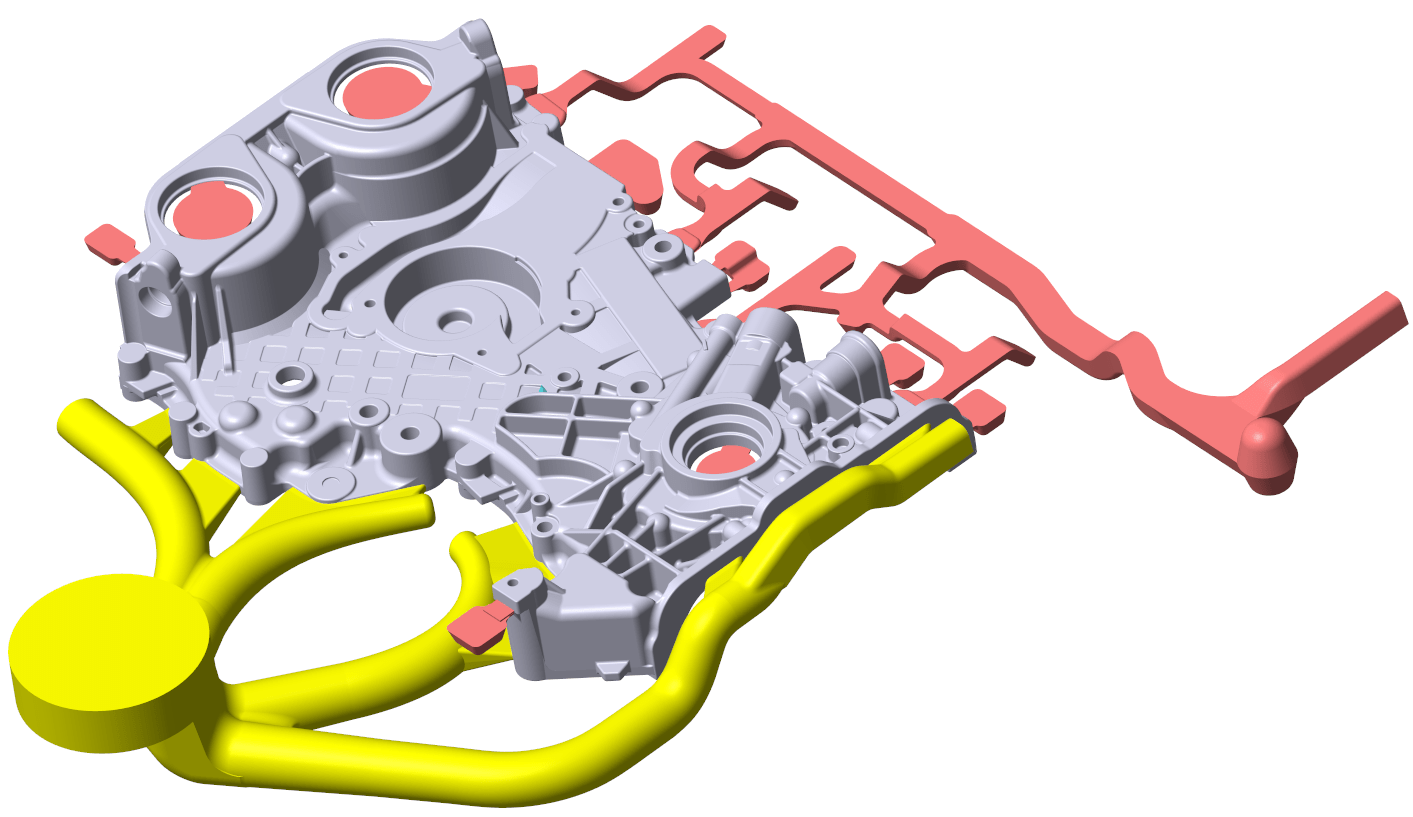
Main objective of using computer-aided casting design and simulation software to casting process is to offer maximum data on casting quality by predicting solidification occurrences and associated features which can be helpful to get an optimum level cast part soundness with maximum defect free component.
The first step involves designing and building a metal die from super alloy. This die creates a same replica of the desired part by injecting melted metal under high or low or vacuum pressure into the cavity. The die can be made as a simple one cavity manual tool or a complex multi-cavity automatic tool depending on volume requirements.
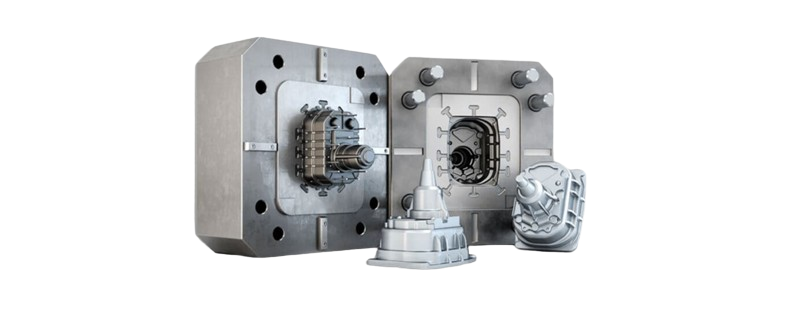

Internal melting chamber will be used for alloying or raw material in the form of ingot or virgin metal where the molten metal will be prepared in internal chamber with the machine itself with proper close chamber-controlled environment so the minimum oxidation process with alloying elements can be done.
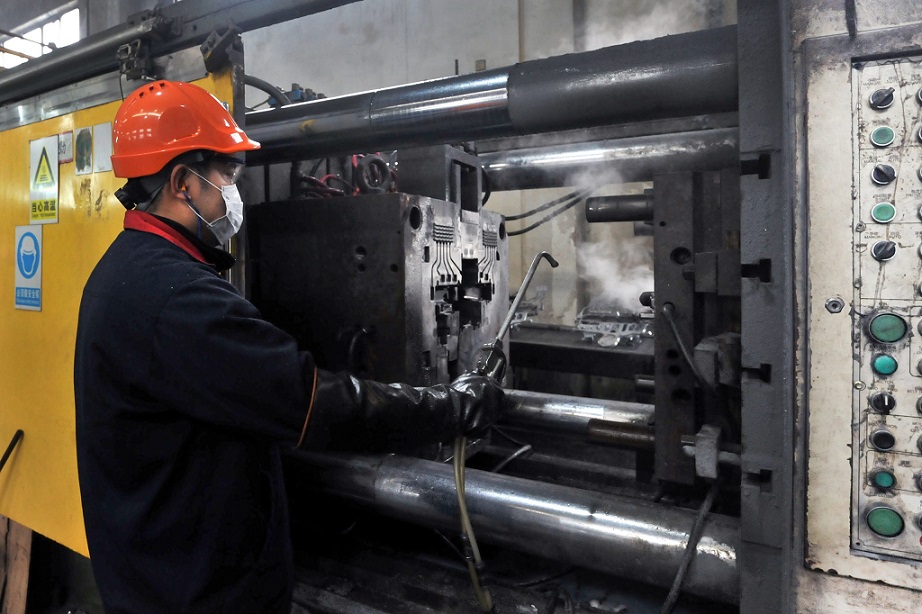
The molten metal has taken place from liquids to superheat temperature as per material requirement then particular desired temperature will be set in chamber then metal injection will be done in mould with certain pressure required as per metal type and during this process mould must be closed or sealed so the entire mirror image of the mould can be taking place net shape of the component.


Parts will be Grind on gating or feeding system with near and net shape matching of the exact cast part then it will be done shot blasting or ceramic blasting as per the material specification or process selection of fettling stage.
The purpose of heat treatment is to change a mechanical property or combination of mechanical properties so that the metal will be more useful, serviceable, and safe for a definite purpose. By heat treating, a metal can be made harder, stronger, and more resistant to impact, heat treatment can also make a metal softer and more ductile.


Parts will be done with super finishing process where some multi-type metal, glass and ceramic media will be used for the process to make a superior level surface finish as per process demand or customer specific requirement point of view.
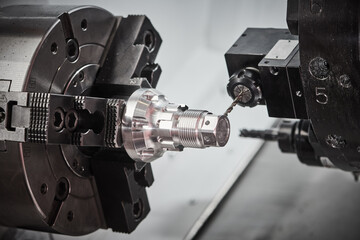
Various machining techniques are then employed including CNC or VMC or HMC or VTL or SPM to achieve the final surface finish & dimensions needed to more important with function, fitment & application area point of view then after with all quality checks & approval before dispatch.

Part will be done with standard or customized packaging systems to make a shipment on desired location by customer, from the beginning level incoterms has been already set for the goods dispatch and clearance of the shipment with particular system & Process.
| Process | Die Moulding - Auto & Manual |
|---|---|
| Present Production | 80 MT Per Month |
| Spare Capacity | 50 MT Per Month |
| Maxi. Weigth Of Single Piece Casting | Few Grams to 5.0 Kilogram |
| Single Piece Size | 500x500x550mm MAX |
| Material | LM2, LM4, LM5, LM6, LM12, LM16, LM21, LM22, LM24, LM25 & Any Special metal in Al. Family. |
| Inspection & Testing Facilities | Spectro Analysis, Mechanical Testing, Hardness Testing's, Impact Testing’s, Micro Tests, Coating & Anodize plant, All NDT Like RT, UT, MT, DT Etc. |
| Sector To Supply | Automobile & Automotive, Aerospace, Defence, Electrical & Electronics, Lighting, Solar Industries, Marine, Medical, Rail & General Engineering Industries |

Pressure die casting is a manufacturing process that uses high pressure to force molten metal into a mold.
The most common materials used in pressure die casting are aluminum alloys, zinc alloys, and magnesium alloys; these are chosen for their good fluidity, ability to produce intricate details, and relatively low melting points, making them suitable for the high-pressure injection process involved in die casting.
At VG Engineering, every casting undergoes a rigorous multi-stage quality control process, including advanced testing and inspection. Our quality assurance measures ensure that each product meets or exceeds industry standards for precision and performance.